Pneumonitis
Pneumonitis
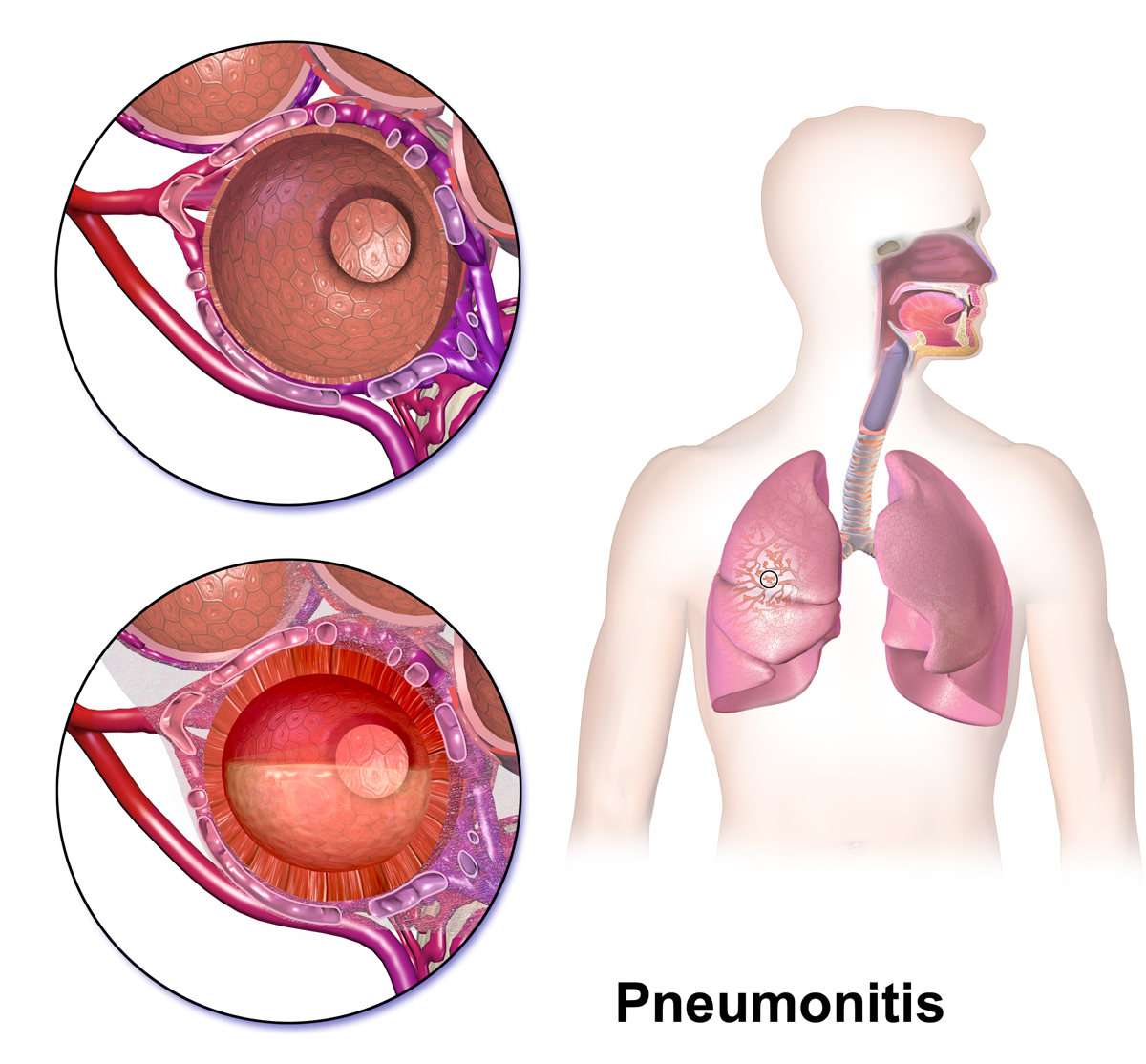
The word ‘Pneumonitis’ is a general term that refers to inflammation (swelling) of lung tissue (alveoli). Although pneumonia is technically a type of pneumonitis because the infection causes inflammation, the term ‘pneumonitis’ is generally used for causes of lung inflammation, other than infections.
Amongst factors that can cause pneumonitis, exposure to airborne irritants are the commonest. Additionally, cancer treatments and many other drugs can cause pneumonitis.
Ayurveda describes types of fevers which resemble the symptoms of pneumonitis. Pneumonitis is a type of inflammation that can be co-related with Shwasanaka Jwara (fever distressing respiration). Similar to the samprapti (progression of disease) of other jwaras (fevers), this condition is a resultant of multiple dosha dushya samoorchana (multi factorial pathogenesis). It is a dukh sadhya vyadhi (difficult to cure) and often leads to death.
Causes Of Pneumonitis
Generally, pneumonitis occurs when any irritating substance cause inflammation (swelling) in the tiny air sacs (called alveoli) of the lungs. This inflammation makes it difficult for oxygen to pass through the alveoli into the bloodstream.
The factors that cause this are –
- Certain drugs.
- Exposure to molds and bacteria.
- Exposure to birds.
- Many radiation treatments
Symptoms Of Pneumonitis
The commonest symptom of pneumonitis is difficulty breathing or shortness of breath – often accompanied by a dry cough. If pneumonitis is not diagnosed or left untreated, it may gradually develop chronic pneumonitis, which can result in scarring in the lungs .
Signs and symptoms of chronic pneumonitis include :
- Difficulty breathing/Shortness of breath
- Coughing
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Unintended weight loss.
Pneumonitis Ayurvedic Treatment
Ahar (Food) and Vihar (regimens) causing Vata and Kapha vitiation should be avoided and a good life style is necessary for better quality of life.
Ayurvedic treatment for Pneumonitis
- Internal medicine
- Panchkarma
- Vamana
- Virechana
- Basti
- Nasya
- Udavartana
- Abhyangam
- Snehan
- Swedan
- Meditation
- Yoga and Pranayama
Diet Recommendations (Aahar)
- Drinking warm water and eating light nutritious food is recommended.
- Soups prepared from moonga, chicken soup and gruels (Khichadi) are recommended.
- Juice extracted from the stem of fresh Giloy (Tinospora cordifolia) may be beneficial.
Diet Recommendations (Aahar)
Eating the right diet may also increase and help retain your memory’s capacity. Leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, spinach and Swiss chard are recommended by some researchers, as are berries, plums, and cherry tomatoes. The Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish like salmon, herring, and anchovies are also thought to help memory retention.
Lifestyle Changes (Vihar)
- Take adequate rest, avoid exertion.
- Avoid cold shower, especially head bath, day sleep, excessive sleep, sedentary life.
- Avoid exposure to molds, bacteria etc in areas that are damp and unkempt.

